Laravel Apps Leaking Secrets
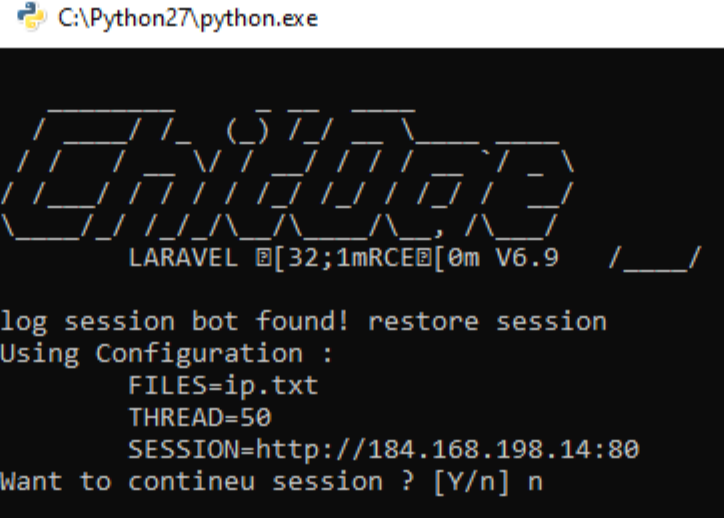
An threat actor logged in through RDP a few days ago to run a “smtp cracker” that scans a list of IP addresses or URLs looking for misconfigured Laravel systems. These attackers are looking for websites that have debug mode enabled, which allows the attacker to see their .env (config) file. The .env file includes AWS, O365, SendGrid, Twilio credentials and more.
The DFIR Report Services
- Private Threat Briefs: Over 20 private DFIR reports annually.
- Threat Feed: Focuses on tracking Command and Control frameworks like Cobalt Strike, Metasploit, Sliver, etc.
- All Intel: Includes everything from Private Threat Briefs and Threat Feed, plus private events, opendir reports, long-term tracking, data clustering, and other curated intel.
- Private Sigma Ruleset: Features 100+ Sigma rules derived from 40+ cases, mapped to ATT&CK with test examples.
- DFIR Labs: Offers cloud-based, hands-on learning experiences, using real data, from real intrusions. Interactive labs are available with different difficulty levels and can be accessed on-demand, accommodating various learning speeds.
Contact us today for pricing or a demo!
What is Laravel?
Laravel is a free, open-source[3] PHP web framework, created by Taylor Otwell and intended for the development of web applications
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laravel
Laravel provides drivers for SMTP, Mailgun, Mandrill, Amazon SES, PHP’s mail function, and sendmail, allowing you to quickly get started sending mail through a local or cloud based service of your choice.
https://laravel.com/docs/5.1/mail
The debug option is turned off by default on Laravel systems, but it appears many users are enabling debug and not understanding the consequences. Here’s an example of debug being enabled (set to true) in the .env config file.
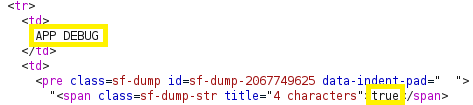
You can check to see if debug is enabled by checking for .env in the web root (site.com/.env) or by sending random data to the webserver and reviewing the response. In the response, you will see the debug option as well as all the information from the .env file, which includes the secrets.
Here’s an example of a web response with debug enabled:

Here’s an example of an .env file:
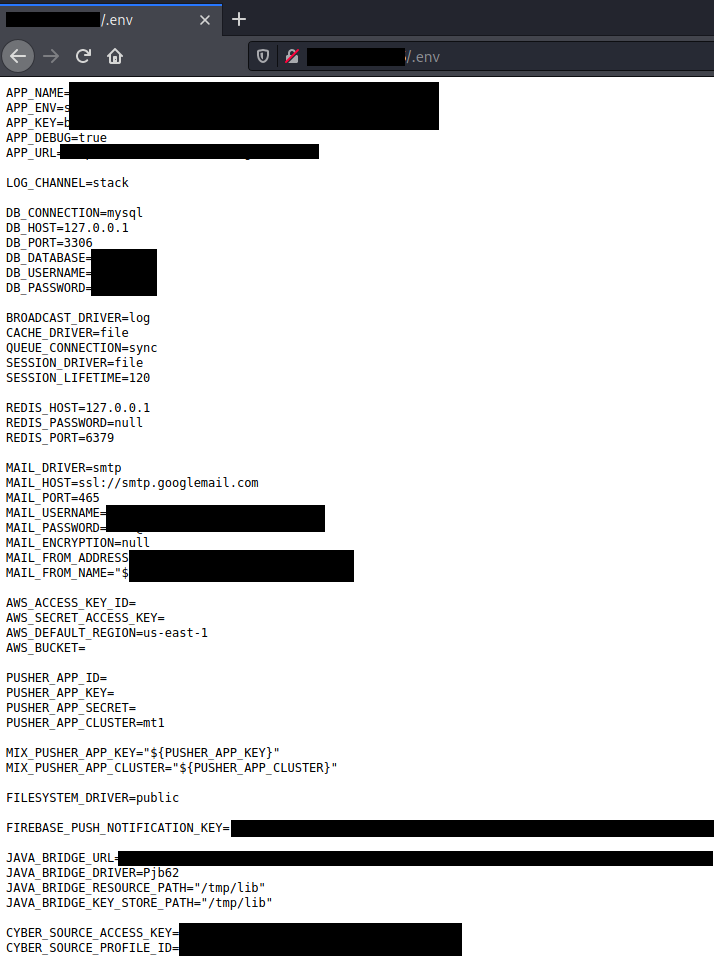
The “smtp cracker” script, which by the way–is not a cracker, and grabs more than just smtp credentials; it uses the above methods to crawl a list of IPs/URLs looking for specific strings in the response such as PayPal, AWS_KEY, SES_KEY, Twilio, sendgrid, office365, zoho, mailgun and others.
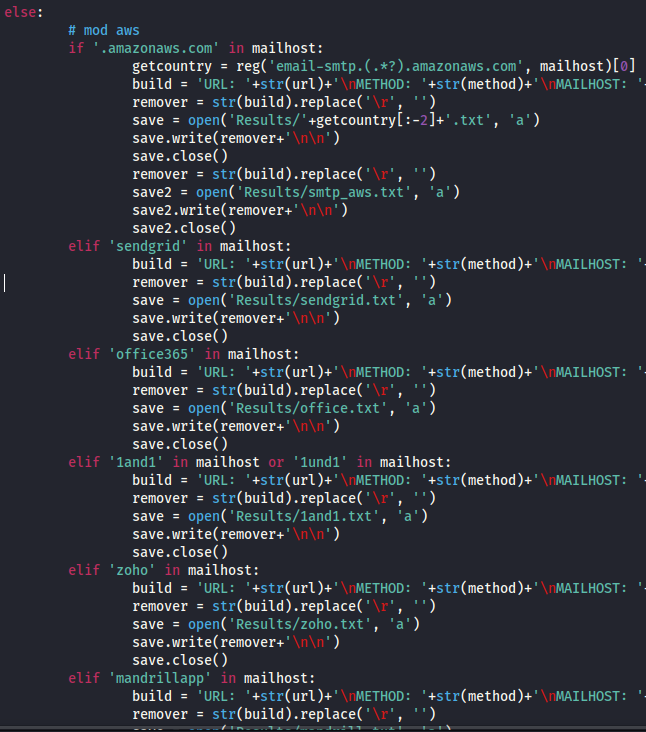
Here’s part of the script, where it looks for a string in mailhost and outputs the secret(s) to the appropriate file.
The output of the script is saved in a folder named Results. The results are divided into groups as seen above.
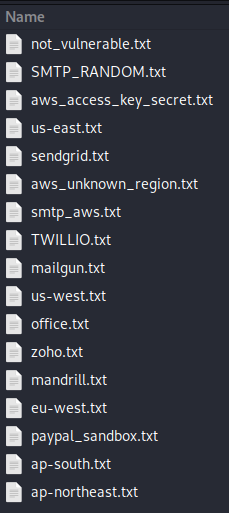
Inside those files contain the secrets and method used to extract the information. This is a partial example of the sendgrid file:
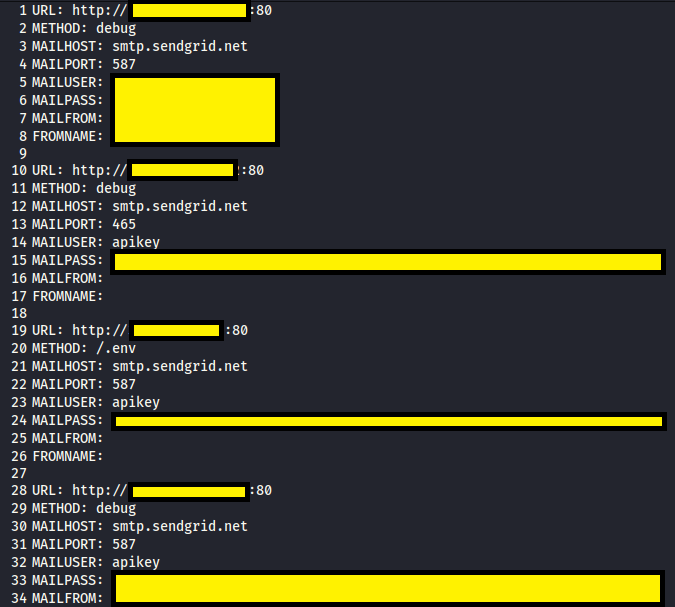
This is a partial example of the office365 text file:
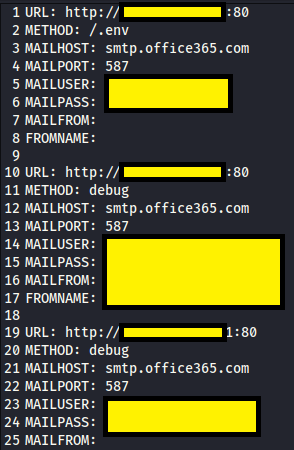
We are in the process of contacting over 100 people/organizations who’s systems are leaking secrets via Laravel debug in hopes that they will remediate the issue and change their passwords. If anyone needs help fixing this issue, please use the Contact Us form to get in touch.
MITRE ATT&CK
Initial Access
RDP login as local administrator from 64.86.198[.]22. No brute force attempts were seen from this IP.
Execution
The attacker installed and used Python 2.7 to execute the smtp cracker script.
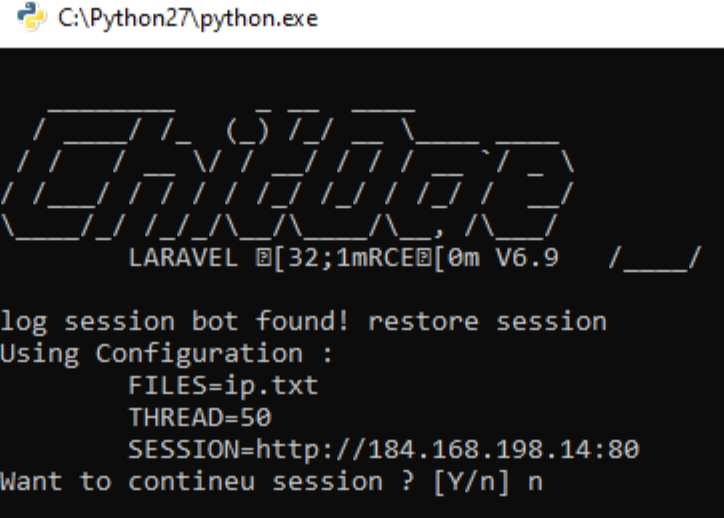
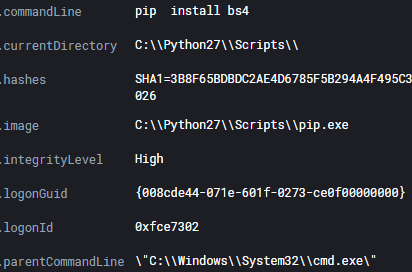
Pip was used to install 4 modules.
pip install requests pip install colorama pip install bs4 pip install tldextract
Detections
Web requests to root/.env or post data that includes 0x[]:androxgh0st (hard coded string in smtp.py)
IOCs
File
| filename | smtp.py |
| md5 | 39e1ec2c704bcdb57034da4ac288446e |
| sha1 | 352e9c78f08574adbaa0aaf49c19d5853bb4be36 |
| sha256 | 478290f801dafc9086810f857c123d74690920a4c44fb573cd01463c1b6fb432 |
Network
| type | value | comment |
| ip-src | 64.86.198.22 | RDP Unauthorized Access |
Valid Accounts - T1078
Python - T1059.006
Scripting - T1064
User Execution - T1204
Graphical User Interface - T1061
Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059